| 编辑推荐: |
本文主要介绍了java 21 新特性。希望能对遇到类似问题的同学有所帮助。
本文来自于微信公众号java知音,由火龙果软件linda编辑、推荐。 |
|
jdk 21 于 2023 年 9 月 19 日发布,是继之前的
lts 版本 jdk 17 之后最新的长期支持 (lts) 版本。在本文中,我们将探讨 jdk 21
新引入的功能。

以下是 jdk 21 的新功能列表:
虚拟线程
序列集合
记录模式
字符串模板(预览)
未命名模式和变量(预览)
未命名类和实例主要方法(预览)
作用域值(预览)
结构化并发(预览) 1虚拟线程
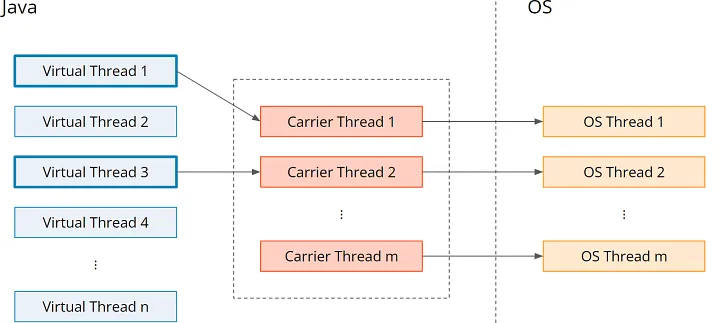
从 java 代码的角度来看,虚拟线程感觉就像普通线程,但它们没有 1:1 映射到操作系统/平台线程。它是从虚拟线程到载体线程进而到操作系统线程的m:n映射。
有一个所谓的载体线程池,虚拟线程临时映射(“安装”)到该线程池上。一旦虚拟线程遇到阻塞操作,虚拟线程就会从载体线程中移除(“卸载”),并且载体线程可以执行另一个虚拟线程(新的或之前被阻塞的虚拟线程)。
载体线程池是forkjoinpool
虚拟线程的一些优点:
提高应用程序吞吐量
提高应用程序可用性
减少内存消耗 创建虚拟线程
要创建虚拟线程,我们可以使用 thread.ofvirtual() 工厂方法并传递可运行对象。
thread.ofvirtual().start(runnable);
thread.ofvirtual().unstarted(runnable);
如果你想让虚拟线程立即启动,你可以使用start() 方法,它会立即执行传递给它的runnable
start()。
如果不希望虚拟线程立即启动,可以使用该unstarted()方法。springboot 虚拟线程,接口吞吐量成倍增加,太爽了!
创建使用虚拟线程的executorservice
我们只需要替换newfixedthreadpool为newvirtualthreadpertaskexecutor
import java.util.concurrent.executorservice;
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
public class virtualthreadexample {
public static void main(string[] args) {
executorservice executor = executors.newvirtualthreadpertaskexecutor();
executor.submit(() -> {
system.out.println(thread.currentthread().getname())
});
executor.shutdown();
}
}
|
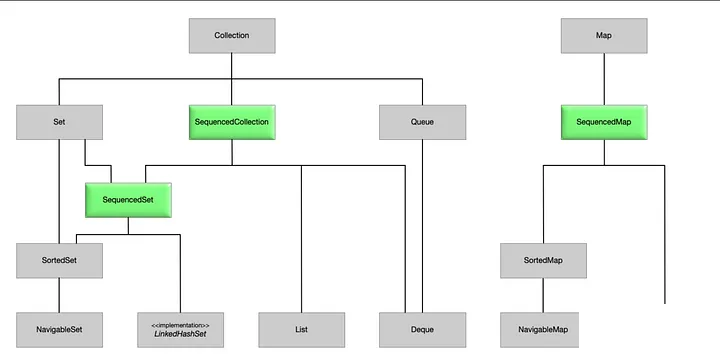
2顺序集合
顺序集合为我们提供了defined encounter order(是一种所见即所得的顺序,含义是从队列中取出元素的顺序既是你存放该元素时候的顺序),用于访问第一个和最后一个元素并以相反的顺序迭代。
这意味着我们可以在集合的两端添加、检索或删除元素。
public interface sequencedcollection<e> extends collection<e> {
default void addfirst(e e) { ... }
default void addlast(e e) { ... }
default e getfirst() { ... }
default e getlast() { ... }
default e removefirst() { ... }
default e removelast() { ... }
sequencedcollection reversed();
}
|
正如我们所看到的,除了reverse()之外的所有方法都是默认方法并提供默认实现。
这意味着现有的集合类(例如 arraylist 和 linkedlist)都可以实现此接口,而无需更改其代码。
arraylist list = new arraylist<>();
list.add(1); // [1]
list.addfirst(0); // [0, 1]
list.addlast(2); // [0, 1, 2]
list.getfirst(); // 0
list.getlast(); // 2
list.reversed(); // [2, 1, 0]
|
sequencedset sequencedset接口对于具有有序元素的 set 非常有用,特别是当您必须执行某些操作(例如检索或删除第一个或最后一个索引处的元素)时。它还提供了一种反转元素的方法。
您还需要知道两个 sequencedset 对象的比较与其他类型的 set 相同,不依赖于元素顺序。
interface sequencedset<e> extends set<e>, sequencedcollection<e> {
sequencedset reversed();
}
|
linkedhashset 是 set 的一个实现,它实现了 sequencedset 接口。
因此,您可以使用 linkedhashset 来创建 sequencedset。
set 的其他实现(例如 hashset 和 treeset)未实现该接口。
让我们探索一些示例来演示如何访问第一个和最后一个元素,以及如何使用反向函数:
sequencedset values = new linkedhashset<>();
values.add("one");
values.add("two");
system.out.println(values); // [one, two]
values.addfirst("zero");
system.out.println(values); // [zero, one, two]
values.addfirst("one");
system.out.println(values); // [one, zero, two]
values.addlast("three");
system.out.println(values); // [one, zero, two, three]
values.removefirst();
system.out.println(values); // [zero, two, three]
sequencedset reversedset = values.reversed();
system.out.println(reversedset); // [three, two, zero]
boolean isequal = values.equals(reversedset);
system.out.println(isequal); // true
system.out.println(values.hashcode()); // 612888
system.out.println(reversedset.hashcode()); // 612888
system.out.println(values.hashcode() == reversedset.hashcode()); // true
|
sequencedmap
如果要使用 sequencedmap 中定义的新方法,则需要使用 map 实现,例如 linkedhashmap
或实现 sortedmap 的 map。
hashmap 不利用 sequenced collections,因为它没有定义 defined
encounter order(是一种所见即所得的顺序,含义是从队列中取出元素的顺序既是你存放该元素时候的顺序)。
interface sequencedmap<k,v> extends map<k,v> {
sequencedmap reversed();
sequencedset sequencedkeyset();
sequencedcollection sequencedvalues();
sequencedset> sequencedentryset();
v putfirst(k, v);
v putlast(k, v);
entry firstentry();
entry lastentry();
entry pollfirstentry();
entry polllastentry();
}
|
在下面的示例中,正如您所看到的,我们可以通过firstentry()和lastentry()方法访问第一个和最后一个元素。
pollfirstentry()方法将删除并返回第一个键值元素,如果映射为空,则返回 null。搜索java知音公众号,回复“java题库”,送你一份java面试宝典
此外,调用reverse()只会比较元素,而不依赖于它们的顺序。
sequencedmap mymap = new linkedhashmap<>();
mymap.put("one", 1);
mymap.put("two", 2);
system.out.println(mymap); // {one=1, two=2}
entry firstentry = mymap.firstentry();
system.out.println(firstentry); // one=1
entry lastentry = mymap.lastentry();
system.out.println(lastentry); // two=2
mymap.putfirst("zero", 0);
system.out.println(mymap); // {zero=0, one=1, two=2}
mymap.putfirst("one", -1);
system.out.println(mymap); // {one=-1, zero=0, two=2}
entry polledfirstentry = mymap.pollfirstentry();
system.out.println(polledfirstentry); // one=-1
system.out.println(mymap); // {zero=0, two=2}
sequencedmap reversedmap = mymap.reversed();
system.out.println(reversedmap); // {two=2, zero=0}
boolean isequal = mymap.equals(reversedmap);
system.out.println(isequal); // true
system.out.println(mymap.hashcode()); // 692224
system.out.println(reversedmap.hashcode()); // 692224
system.out.println(mymap.hashcode() == reversedmap.hashcode()); // true
|
3字符串模板
这是预览功能,默认禁用,我们需要使用
--enable-preview启用字符串模板。
首先,在深入探讨字符串模板之前,我将探讨一些用于组合字符串的技术。
(加号)运算符:最大的缺点是每次使用 运算符时都会创建一个新字符串。
stringbuffer 和 stringbuilder: stringbuffer 是线程安全的,而
stringbuilder 是在 java 5 中添加的,性能更高,但不是线程安全的替代方案。
它们的主要缺点是冗长,尤其是对于更简单的字符串:
var greeting = new stringbuilder()
.append("hello, welcome ")
.append(name)
.tostring();
|
string::format 和 string::formatter: 它们允许可重用模板,但它们要求我们指定格式并以正确的顺序提供变量。
var format = "good morning %s, it's a beautiful day!";
var text = string.format(format, name);
// java 15
var text = format.formatter(name);
|
尽管我们节省了字符串分配的数量,但现在 jvm 必须解析/验证模板字符串。
java.text.messageformat: 与string格式相同,但更详细
var format = new messageformat("good morning {0}, it's a beautiful day!");
var greeting = format.format(name);
|
现在我们有字符串模板来拯救
它简单、简洁,处理字符串的新方法称为模板表达式。它们可以执行插值,还为我们提供了组合字符串的灵活性,并将结构化文本转换为任何对象,而不仅仅是字符串。
模板表达式由三个组成部分组成:
模板处理器:java 提供了两种用于执行字符串插值的模板处理器:str 和 fmt
包含包装表达式的模板,如 {name}
点 (.) 字符
以下是一些关于如何将字符串模板与模板处理器一起使用的示例:
package com.mina.stringtemplates;
import static java.util.formatprocessor.fmt;
import java.time.localdate;
import java.time.format.datetimeformatter;
public class stringtemplateexamples {
public static string greeting(string firstname, string lastname) {
return str."hello! good morning \{ firstname } \{ lastname }" ;
}
public static string multiplywitharithmeticexpressions(int a, int b) {
return str."\{ a } times \{ b } = \{ a * b }" ;
}
public static string multiplywithjavaexpression(int a, int b) {
return str."\{ a } times \{ b } = \{ math.multiplyexact(a, b) }" ;
}
// multiplication with floating point numbers rounded to two decimal places using the fmt template processor
public static string multiplyfloatingnumbers(double a, double b) {
return fmt."%.2f\{ a } times %.2f\{ b } = %.2f\{ a * b }" ;
}
public static string geterrorresponse(int httpstatus, string errormessage) {
return str."""
{
"httpstatus": \{ httpstatus },
"errormessage": "\{ errormessage }"
}""" ;
}
public static string getcurrentdate() {
return str."today's date: \{
localdate.now().format(
datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy-mm-dd")
) }" ;
}
}
|
4记录模式
记录模式匹配是一种在单个步骤中匹配记录类型并访问其组件的方法。
我们用它来测试一个值是否是记录类类型的实例,如果是,则对其组件值执行模式匹配。
下面的示例测试是否是具有记录模式transaction的记录实例transactiontransaction(string
type, double amount)
package com.mina.recordpattern;
public class recordpatternexample {
// i'm using "_" for readability here, this won't compile
public static string gettransactiontype(transaction transaction) {
return switch (transaction) {
case null -> throw new illegalargumentexception("transaction can not be null.");
case transaction(string type, double amount) when type.equals("deposit") && amount > 0 -> "deposit";
case transaction(string type, _) when type.equals("withdrawal") -> "withdrawal";
default -> "unknown transaction type";
};
}
record transaction(string type, double amount) {
}
}
|
如果事务为空,会发生什么?你是对的——抛出了一个空指针异常。这也是java 21中的情况,但是现在我们可以通过写case
null->来显式地使用null case,这样可以避免nullpointerexception。
保护模式:也可以保护特定情况。例如,我们使用when关键字来检查相等性。
搜索java知音公众号,回复“java题库”,送你一份java面试宝典
5switch 模式匹配
switch模式匹配在 java 17 中作为预览功能引入,并在 java 21 中永久保留。
语句switch将控制转移到多个语句或表达式之一,具体取决于其选择器表达式的值(可以是任何类型),并且case标签可以具有模式。
它检查其选择器表达式是否与模式匹配,与测试其选择器表达式是否完全等于常量相比,这更具可读性和灵活性。
package com.mina.switchpatternmatching;
import com.mina.switchpatternmatching.switchpatternmatchingexample.transaction.deposit;
import com.mina.switchpatternmatching.switchpatternmatchingexample.transaction.withdrawal;
public class switchpatternmatchingexample {
public static string gettransactiontype(transaction transaction) {
return switch (transaction) {
case null:
throw new illegalargumentexception("transaction can't be null.");
case deposit deposit when deposit.getamount() > 0: // guarded pattern with when clause
yield "deposit";
case withdrawal withdrawal:
yield "withdrawal";
default:
yield "unknown transaction type";
};
}
sealed class transaction permits deposit, withdrawal {
private double amount;
public transaction(double amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public double getamount() {
return amount;
}
final class withdrawal extends transaction {
public withdrawal(double amount) {
super(amount);
}
}
final class deposit extends transaction {
public deposit(double amount) {
super(amount);
}
}
}
}
|
希望这篇文章可以帮助您更好地了解 java 21 的新功能!
| 